For New Scientist, 18 April 2015: a review of the 2015 Designs of the Year competition at London’s Design Museum.
In friendly competition with Percy Bysshe Shelley, the poet Horace Smith once wrote a poem entitled Ozymandias. Shelley’s version is the one we remember, but Smith’s is compelling for another reason. He imagines a hunter traipsing through the ruins of a future London. Lighting upon a fragment of a monument, he “stops to guess/What powerful but unrecorded race/Once dwelt in that annihilated place”.
This year’s Designs of the Year competition has its monumental entries, but even the most grandiloquent of the 76 nominations at least tips its hat to the idea that the world will not sustain another great ruin, or may end up our next great ruin, unless we respond more cleverly to our environment.
Jean Nouvel’s One Central Park in Sydney, Australia, towers above its architectural competitors, literally. Clad in climbing plants by Patrick Blanc, the leading designer of vertical gardens, One Central’s overriding purpose seems to be to apologise for its very existence.
There is even a motorised heliostat mounted on a cantilever near the roof, to erase the building’s shadow. The arrangement looks terrifying in photographs, suggesting the 50-metre-high moon towers of the 19th century when towns experimented with civic lighting.
In Ho Chi Minh City, a project called House for Trees eschews apology for action, albeit of a most eccentric sort. Here, high-density living units double as gigantic containers for tropical trees. Come the rains, a sufficient number of these properties could reduce the risk of urban flooding. At least, so claim architects Vo Trong Nghia, although it sounds like special pleading to me – an alibi for the strange green dream they’re weaving, of wandering lost among giant plant pots.
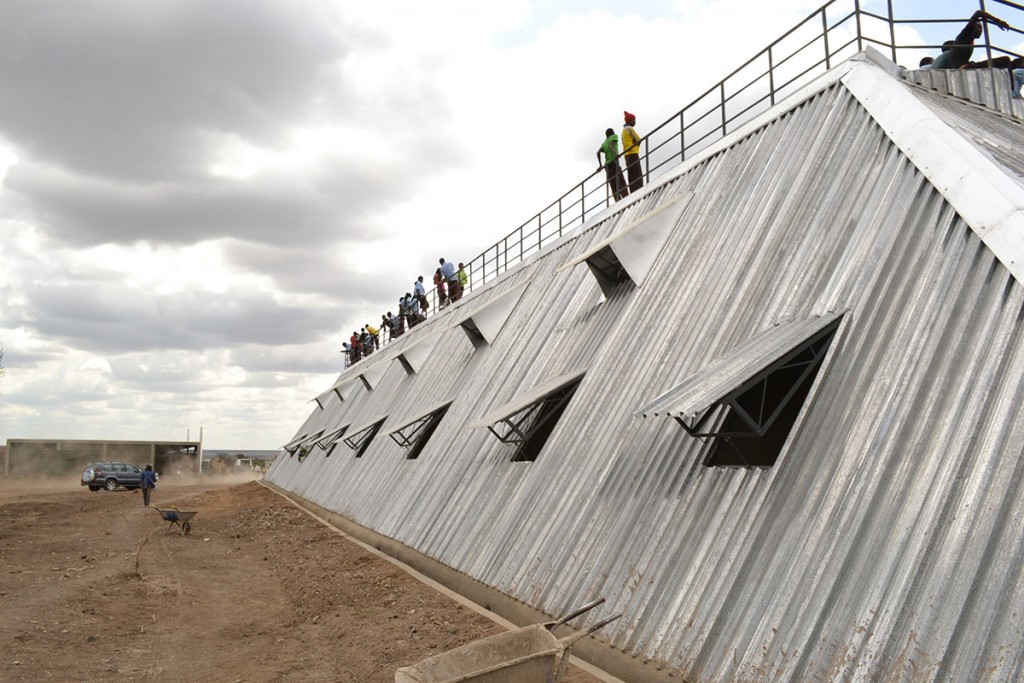
Where rains are few, a more down to earth aesthetic holds sway. PITCHAfrica’s Waterbank Campus is a 10-acre school site in Laikipia, Kenya, where 4 acres of irrigated conservation agriculture are fed by 7 low-cost buildings, designed to collect and store what little precipitation there is.
PITCHAfrica’s vision extends beyond unassuming architecture to provide resources like clean water, food and sanitation on-site for its students, in the hope they will spread the word about how to manage scarce resources at home.
This vision, of an artificial “ecosystem capable of empowering and transforming communities”, is shared by a great many of the show’s “technical fix” entries. Take the Blue Diversion toilet. This project, led by the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, and funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, is an all-in-one sanitation, fertiliser, drinking-water and biogas solution. In this cheap, ugly, blue plastic toilet, nothing is wasted – not even sunlight; there’s a small solar panel on its roof.
Other ideas plug in to the smog and mess of cities, and try to make daily life a little more bearable. At the University of Engineering and Technology, Lima, Peru, researchers have invented a billboard that purifies the air in a five-block radius, scrubbing it clean of construction dust and 99 per cent of airborne bacteria – it would take 1200 trees to do the equivalent work, says the team.
Another entry, The Ocean Cleanup, designed by Erwin Zwart with Boyan Slat and Jan de Sonneville, tackles the plastic garbage circulating the world’s oceans. Why not string barriers over the waves to catch the plastic as it moves around? Having raised over U$2 million through crowdfunding, the organisation plans to construct and test large-scale pilot projects.
This is technical fixery at its purest. It doesn’t prevent the oceans being littered: it is an environmental sticking plaster, permitting us to pursue business as usual. But why should designers have to carry the whole world on their shoulders? Designs like these could be part of a broader, political solution. The Ocean Cleanup’s barriers would be a fitting monument for our descendants to puzzle over.
Better, of course, to avoid collapse entirely, but it won’t be simple. It is easier for designers to ameliorate or even disguise problems, rather than to address them head on. Two projects built around the food supply demonstrate this neatly.
Disclosed, by Marion Ferrec at the Royal College of Art, in collaboration with Kate Wakely, is a web-based consumer service that allows you to choose products according to your health needs and ethical preferences. Lacking vast wealth, leisure and self-absorption, I won’t be using it.
But neither am I entirely persuaded by Marcel’s humorous campaign for the French supermarket giant Intermarché – a series of beautifully photographed imperfect fruits and vegetables. The idea is to shift ridiculous-looking potatoes, hideous oranges and failed lemons onto the consumer, and thereby reduce food waste. But the campaign preserves and reinforces (by price offers) the very distinction between perfect and imperfect produce that caused the problem in the first place.
It is, frankly, next to impossible to imagine how we get from a wasteful here to a sustainable there – and for that reason alone, I think Alexandra Daisy Ginsberg’s design fiction Designing for the Sixth Extinction is the poster-child of this year’s competition. Ginsberg has anatomised the ultimate disruptive enterprise, in which “nature is totally industrialized for the benefit of society”.
Although her fictional synthetic creatures are deliciously creepy (especially the “biologically-powered mobile soil bioremediation device”) it is her business model of saving our civilisation at the expense of the natural world, while replacing it with something better, that fascinates.
If Ginsberg’s vision comes to pass, our descendants won’t be able to puzzle at our monuments. Our monuments will be everywhere, all around them, and inside them.